躲在 LVS 后面,如何平滑的上下线是个问题
正常上线流程:
- Controller、Nginx 正常运行
- 加到 LVS 后面
- 应用流量接进来
正常下线流程:
- 从 LVS 摘掉
- 应用请求结束
- Controller、Nginx 退出
官方默认的配置肯定做不到。
方案 1:
利用 Kubernetes 生命周期钩子,平滑上下线。
- 启动 postStart,
touch status.html - 结束 preStop,
remove status.html
听起来可行,但是没有办法做到正常上线,因为不知道啥时候 Controller、Nginx 准备好。
Nginx 启动正常不代表 Controller 启动正常。
方案 2:
在 location 里写 Lua。
结合生命周期钩子,通过判断传递的参数,来执行 check 逻辑,模拟默认健康检查流程。
听起来也可行,但需要复现 Start()、Stop() 逻辑,太 trick 了,不好维护。
check 逻辑:
// Check returns if the nginx healthz endpoint is returning ok (status code 200)
func (n *NGINXController) Check(_ *http.Request) error {
if n.isShuttingDown {
return fmt.Errorf("the ingress controller is shutting down")
}
// check the nginx master process is running
fs, err := proc.NewFS("/proc", false)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "reading /proc directory")
}
f, err := ioutil.ReadFile(nginx.PID)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "reading %v", nginx.PID)
}
pid, err := strconv.Atoi(strings.TrimRight(string(f), "\r\n"))
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "reading NGINX PID from file %v", nginx.PID)
}
_, err = fs.NewProc(pid)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "checking for NGINX process with PID %v", pid)
}
statusCode, _, err := nginx.NewGetStatusRequest(nginx.HealthPath)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "checking if NGINX is running")
}
if statusCode != 200 {
return fmt.Errorf("ingress controller is not healthy (%v)", statusCode)
}
statusCode, _, err = nginx.NewGetStatusRequest("/is-dynamic-lb-initialized")
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrapf(err, "checking if the dynamic load balancer started")
}
if statusCode != 200 {
return fmt.Errorf("dynamic load balancer not started")
}
return nil
}
最终方案: 添加 lvscheck server,严格匹配。
server {
server_name lvscheck;
listen 80;
location ~* "^/status$" {
rewrite ^/status$ /healthz break;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:10254;
}
}
Start() 的逻辑是满足需求的,因为会配置健康检测与存活检测以应对 LVS。
// Start starts a new NGINX master process running in the foreground.
func (n *NGINXController) Start() {
klog.Info("Starting NGINX Ingress controller")
n.store.Run(n.stopCh)
// we need to use the defined ingress class to allow multiple leaders in order to update information about ingress status
electionID := fmt.Sprintf("%v-%v", n.cfg.ElectionID, class.DefaultClass)
if class.IngressClass != "" {
electionID = fmt.Sprintf("%v-%v", n.cfg.ElectionID, class.IngressClass)
}
setupLeaderElection(&leaderElectionConfig{
Client: n.cfg.Client,
ElectionID: electionID,
OnStartedLeading: func(stopCh chan struct{}) {
if n.syncStatus != nil {
go n.syncStatus.Run(stopCh)
}
n.metricCollector.OnStartedLeading(electionID)
// manually update SSL expiration metrics (to not wait for a reload)
n.metricCollector.SetSSLExpireTime(n.runningConfig.Servers)
},
OnStoppedLeading: func() {
n.metricCollector.OnStoppedLeading(electionID)
},
PodName: n.podInfo.Name,
PodNamespace: n.podInfo.Namespace,
})
cmd := n.command.ExecCommand()
// put NGINX in another process group to prevent it to receive signals meant for the controller
cmd.SysProcAttr = &syscall.SysProcAttr{
Setpgid: true,
Pgid: 0,
}
if n.cfg.EnableSSLPassthrough {
n.setupSSLProxy()
}
klog.Info("Starting NGINX process")
n.start(cmd)
go n.syncQueue.Run(time.Second, n.stopCh)
// force initial sync
n.syncQueue.EnqueueTask(task.GetDummyObject("initial-sync"))
// In case of error the temporal configuration file will be available up to five minutes after the error
go func() {
for {
time.Sleep(5 * time.Minute)
err := cleanTempNginxCfg()
if err != nil {
klog.Infof("Unexpected error removing temporal configuration files: %v", err)
}
}
}()
if n.validationWebhookServer != nil {
klog.Infof("Starting validation webhook on %s with keys %s %s", n.validationWebhookServer.Addr, n.cfg.ValidationWebhookCertPath, n.cfg.ValidationWebhookKeyPath)
go func() {
klog.Error(n.validationWebhookServer.ListenAndServeTLS("", ""))
}()
}
for {
select {
case err := <-n.ngxErrCh:
if n.isShuttingDown {
break
}
// if the nginx master process dies the workers continue to process requests, passing checks but in case of updates in ingress no updates will be reflected in the nginx configuration which can lead to confusion and report issues because of this behavior.
// To avoid this issue we restart nginx in case of errors.
if process.IsRespawnIfRequired(err) {
process.WaitUntilPortIsAvailable(n.cfg.ListenPorts.HTTP)
// release command resources
cmd.Process.Release()
// start a new nginx master process if the controller is not being stopped
cmd = n.command.ExecCommand()
cmd.SysProcAttr = &syscall.SysProcAttr{
Setpgid: true,
Pgid: 0,
}
n.start(cmd)
}
case event := <-n.updateCh.Out():
if n.isShuttingDown {
break
}
if evt, ok := event.(store.Event); ok {
klog.V(3).Infof("Event %v received - object %v", evt.Type, evt.Obj)
if evt.Type == store.ConfigurationEvent {
// TODO: is this necessary? Consider removing this special case
n.syncQueue.EnqueueTask(task.GetDummyObject("configmap-change"))
continue
}
n.syncQueue.EnqueueSkippableTask(evt.Obj)
} else {
klog.Warningf("Unexpected event type received %T", event)
}
case <-n.stopCh:
break
}
}
}
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
但 Stop() 逻辑不满足需求,无法做到先从 LVS 摘掉,再停止服务。
这里有一个很关键的点是,健康检测为 false 不等于将其从 LVS 摘掉。
如果 LVS 的健康检测周期是 8s,累计 3 次失败再摘掉的话,需要 24s 才能停止服务,但 Controller + Nginx 停止服务的速度远比这快。
所以,需要延迟停止服务的策略。
// Stop gracefully stops the NGINX master process.
func (n *NGINXController) Stop() error {
n.isShuttingDown = true
n.stopLock.Lock()
defer n.stopLock.Unlock()
if n.syncQueue.IsShuttingDown() {
return fmt.Errorf("shutdown already in progress")
}
klog.Info("Shutting down controller queues")
close(n.stopCh)
go n.syncQueue.Shutdown()
if n.syncStatus != nil {
n.syncStatus.Shutdown()
}
if n.validationWebhookServer != nil {
klog.Info("Stopping admission controller")
err := n.validationWebhookServer.Close()
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
var (
period int
perr error
)
periodEnv := os.Getenv("GRACE_STOP_PERIOD")
if period, perr = strconv.Atoi(periodEnv); perr != nil {
period = 30
}
klog.Infof("Graceful waiting %d second to stop", period)
time.Sleep(time.Second * time.Duration(period))
// send stop signal to NGINX
klog.Info("Stopping NGINX process")
cmd := n.command.ExecCommand("-s", "quit")
cmd.Stdout = os.Stdout
cmd.Stderr = os.Stderr
err := cmd.Run()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// wait for the NGINX process to terminate
timer := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 1)
for range timer.C {
if !nginx.IsRunning() {
klog.Info("NGINX process has stopped")
timer.Stop()
break
}
}
return nil
}
默认也有 preStop 逻辑,但没有什么帮助:
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command:
- /wait-shutdown
开始造轮子,做一个 low 版的延迟停止:
// Stop gracefully stops the NGINX master process.
func (n *NGINXController) Stop() error {
...
periodEnv := os.Getenv("GRACE_STOP_PERIOD")
if period, perr = strconv.Atoi(periodEnv); perr != nil {
period = 30
}
klog.Infof("Graceful waiting %d second to stop", period)
time.Sleep(time.Second * time.Duration(period))
...
}
Header 携带问题
PHP 需要解析 x-real-ip 字段中的特殊标识来获取到真实的 IP。
获取真实 IP 的途径有如下几种:
x-real-ipx-forwarded-for中的$remote_addr- Header 增加特殊字段
如果尽量兼容现有的方式,整体代价又最小,修改 nginx.conf 可能是最简单的方式。
$remote_addr 不能伪造,需要修改内核,又是 trick 的方式,快算了。
set $q8s_remote_addr $remote_addr;
if ( $http_x_real_ip != "" ) {
set $q8s_remote_addr $http_x_real_ip;
}
{{ $proxySetHeader }} X-Real-IP $q8s_remote_addr;
Nginx 里只有 if,没有 else。
ngx.var 搞定一切。ngx.ctx 相对昂贵。
请认真学习
nginx.conf与 Lua,否则 OpenResty 分分钟告诉你who's your daddy。
超时太长
s -> ms
proxy_connect_timeout {{ $location.Proxy.ConnectTimeout }}ms;
原本也是想挂载 nginx.tmpl 的,但考虑到 nginx.tmpl 修改后需要测试,不能动态生效,所以放弃了挂载方式。
修改日志格式,改用 Lua 记录
plugin 需要有效利用:
init_by_lua_block {
-- load all plugins that'll be used here
plugins.init({"json_log"})
}
先读源码,不然分分钟告诉你
who's your daddy。
local string_format = string.format
local new_tab = require "table.new"
local ngx_log = ngx.log
local INFO = ngx.INFO
local ERR = ngx.ERR
local _M = {}
local MAX_NUMBER_OF_PLUGINS = 10000
-- TODO: is this good for a dictionary?
local plugins = new_tab(MAX_NUMBER_OF_PLUGINS, 0)
local function load_plugin(name)
local path = string_format("plugins.%s.main", name)
local ok, plugin = pcall(require, path)
if not ok then
ngx_log(ERR, string_format("error loading plugin \"%s\": %s", path, plugin))
return
end
plugins[name] = plugin
end
function _M.init(names)
for _, name in ipairs(names) do
load_plugin(name)
end
end
function _M.run()
local phase = ngx.get_phase()
for name, plugin in pairs(plugins) do
if plugin[phase] then
ngx_log(INFO, string_format("running plugin \"%s\" in phase \"%s\"", name, phase))
-- TODO: consider sandboxing this, should we?
-- probably yes, at least prohibit plugin from accessing env vars etc
-- but since the plugins are going to be installed by ingress-nginx operator they can be assumed to be safe also
local ok, err = pcall(plugin[phase])
if not ok then
ngx_log(ERR, string_format("error while running plugin \"%s\" in phase \"%s\": %s", name, phase, err))
end
end
end
end
return _M
先了解啥是 ngx.get_phase(),来自温主席的书:
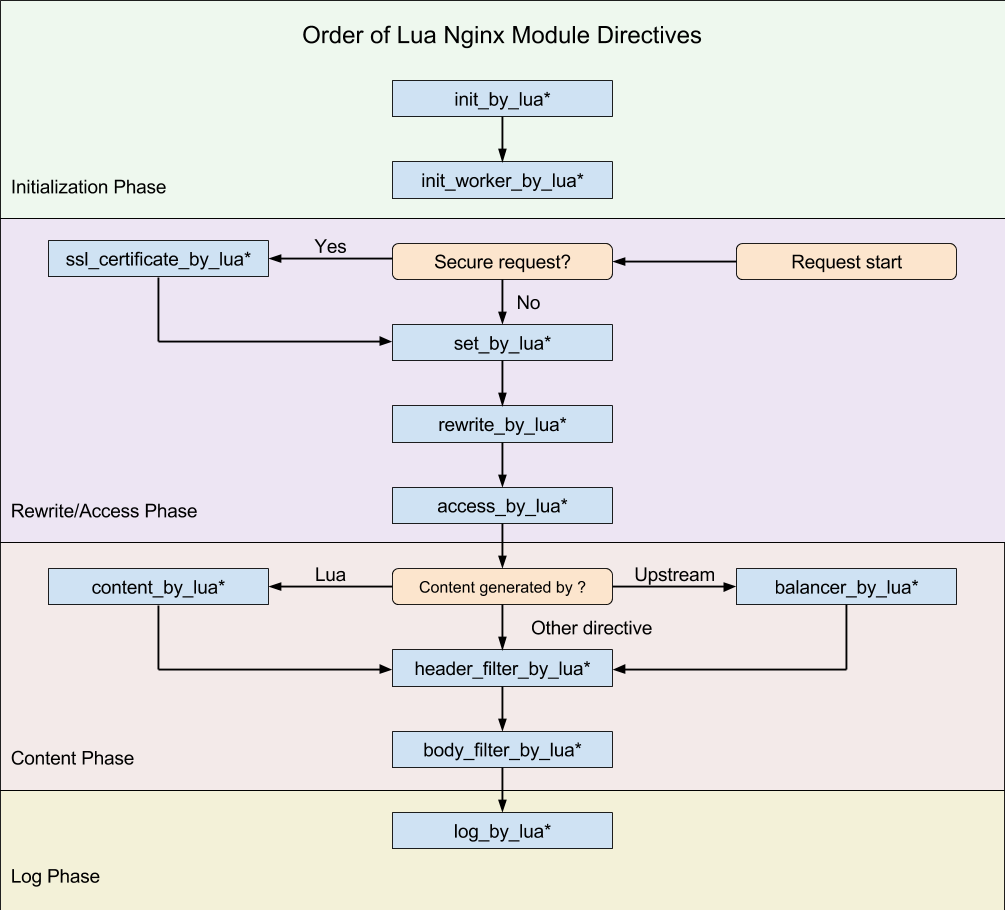
set_by_lua流程分支处理判断变量初始化rewrite_by_lua转发、重定向、缓存等功能(例如特定请求代理到外网)access_by_luaIP 准入、接口权限等情况集中处理(例如配合 iptable 完成简单防火墙)content_by_lua内容生成header_filter_by_lua响应头部过滤处理(例如添加头部信息)body_filter_by_lua响应体过滤处理(例如完成应答内容统一成大写)log_by_lua会话完成后本地异步完成日志记录(日志可以记录在本地,还可以同步到其他机器)
官方文档: https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#ngxget_phase
在 Ingress 里的调用:
init_worker_by_lua_block {
plugins.run()
}
rewrite_by_lua_block {
plugins.run()
}
header_filter_by_lua_block {
plugins.run()
}
log_by_lua_block {
plugins.run()
}
自定义 log 形态:
local json = require("cjson")
local ngx_re = require("ngx.re")
local req = ngx.req
local var = ngx.var
local function gsub(subject, regex, replace)
return ngx.re.gsub(subject, regex, replace, "jo")
end
local function get_upstream_addrs()
local res = {}
setmetatable(res, json.empty_array_mt)
local cnt = 0
for k, v in ipairs(ngx_re.split(var.upstream_addr, ","))
do
res[k] = gsub(v, [[^%s*(.-)%s*$]], "%1")
cnt = k
end
return res, cnt
end
local _M = {}
function _M.log()
local log = {
hostname = var.hostname,
request_method = var.request_method,
request_uri = gsub(var.request_uri, [[\?.*]], ""),
args = req.get_uri_args(),
headers = req.get_headers(),
remote_addr = var.remote_addr,
uri = var.uri,
upstream_bytes_sent = tonumber(var.upstream_bytes_sent),
upstream_bytes_received = tonumber(var.upstream_bytes_received),
upstream_status = tonumber(var.upstream_status),
upstream_connect_time = tonumber(var.upstream_connect_time),
upstream_header_time = tonumber(var.upstream_header_time),
upstream_response_time = tonumber(var.upstream_response_time),
body_bytes_sent = tonumber(var.body_bytes_sent),
bytes_sent = tonumber(var.bytes_sent),
status = tonumber(var.status),
connection_requests = tonumber(var.connection_requests),
request_time = tonumber(var.request_time),
time_local = ngx.time()
}
log.upstream_addr, log.upstream_tries = get_upstream_addrs()
var.json_log = gsub(json.encode(log), [[\\/]], "/")
end
return _M
escape=json 是 OpenResty 1.11.8 以后的新特性:
log_format upstreaminfo escape=none '$json_log';
落地配置
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx-redefine
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: '10254'
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: 'false'
spec:
serviceAccountName: ingress-nginx-redefine-serviceaccount
hostNetwork: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: nginx-ingress-controller:0.26.1
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- '--configmap=default/ingress-nginx-redefine-configuration'
- '--default-backend-service=default/ingress-default-http-backend'
- '--annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io'
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: GRACE_STOP_PERIOD
value: '30'
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
hostPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
hostPort: 443
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command:
- /wait-shutdown
resources:
limits:
cpu: 0
memory: 0
requests: {}
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/ingress
operator: Exists
tolerations:
- operator: Exists